Here’s an overview of the structure and working principle of a dry-type transformer.
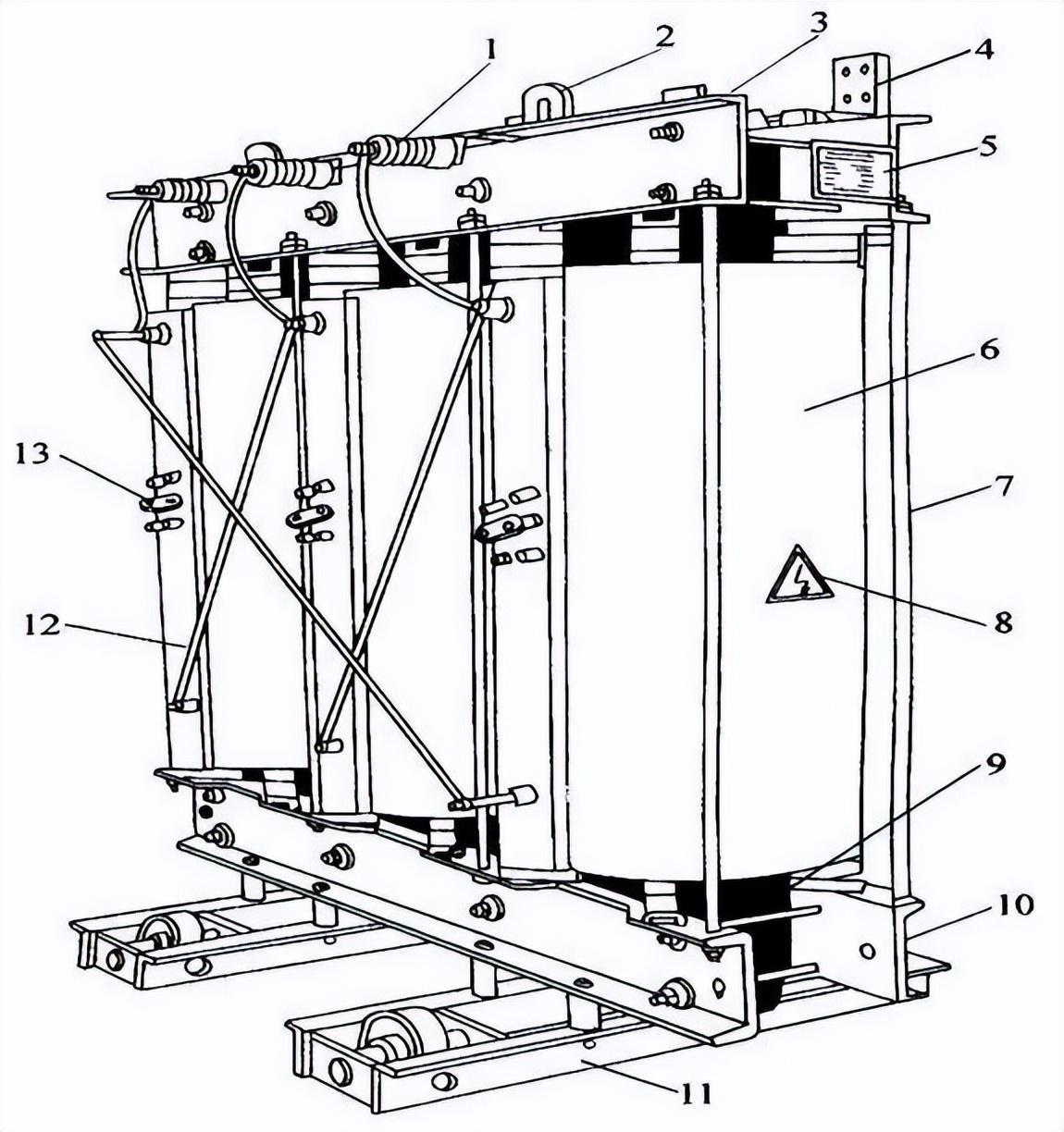
Structure and Working Principle of Dry-Type Transformer
Structure:
A dry-type transformer, also known as a cast resin transformer, features a design without the use of liquid insulating materials like oil or silicone. Instead, it employs solid insulation materials, typically epoxy resin, to encapsulate the windings and core.
The primary and secondary windings, made of insulated copper or aluminum conductors, are wound around the core. The core is often constructed from high-grade, grain-oriented silicon steel laminations. The entire assembly is then enclosed within a robust casing to shield it from environmental factors and provide insulation.
Working Principle:
The operational principle of a dry-type transformer is identical to that of a conventional transformer, based on electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it produces a changing magnetic field around the core. This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
The absence of liquid insulation renders dry-type transformers suitable for indoor applications where safety, environmental concerns, or space constraints preclude the use of oil-filled transformers.
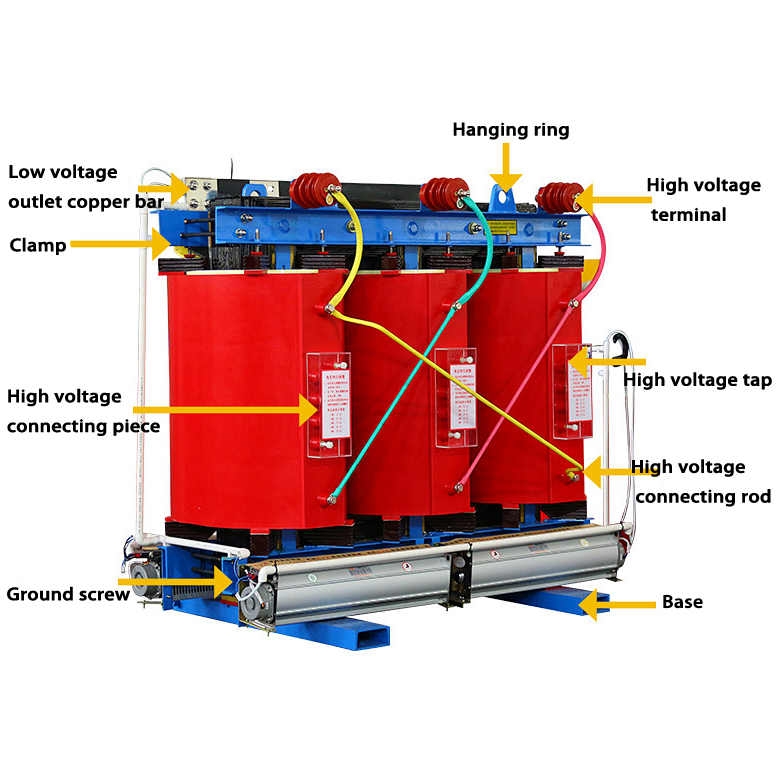
Advantages:
Safety: Dry-type transformers eliminate the risk of oil leaks and fire hazards associated with liquid-filled transformers, enhancing safety for indoor installations.
Environmental Friendliness: As dry-type transformers do not contain oil, they are environmentally friendly and comply with stringent regulations concerning hazardous substances.
Maintenance-Free Operation: The solid insulation and sealed enclosure of dry-type transformers reduce the need for maintenance, enhancing reliability and cost-effectiveness over their lifespan.
Applications:
Dry-type transformers find common use in various indoor applications, including commercial buildings, hospitals, data centers, and industrial facilities. They are preferred in locations where fire safety regulations are strict or where space is at a premium.
Environmental Considerations:
The environmental benefits of dry-type transformers include:
Reduced Fire Risk: The absence of flammable liquids like oil eliminates the risk of fire propagation in case of transformer failure.
Minimal Environmental Impact: Dry-type transformers do not pose environmental hazards associated with oil spills or leaks. They are compliant with regulations governing hazardous substances and are suitable for environmentally sensitive areas.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, dry-type transformers offer efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly solutions for electrical power distribution in indoor settings. Their solid insulation, effective cooling mechanisms, and protective features make them indispensable components in various applications across industries.




